07 Aug Case of the Week 8/05/2024
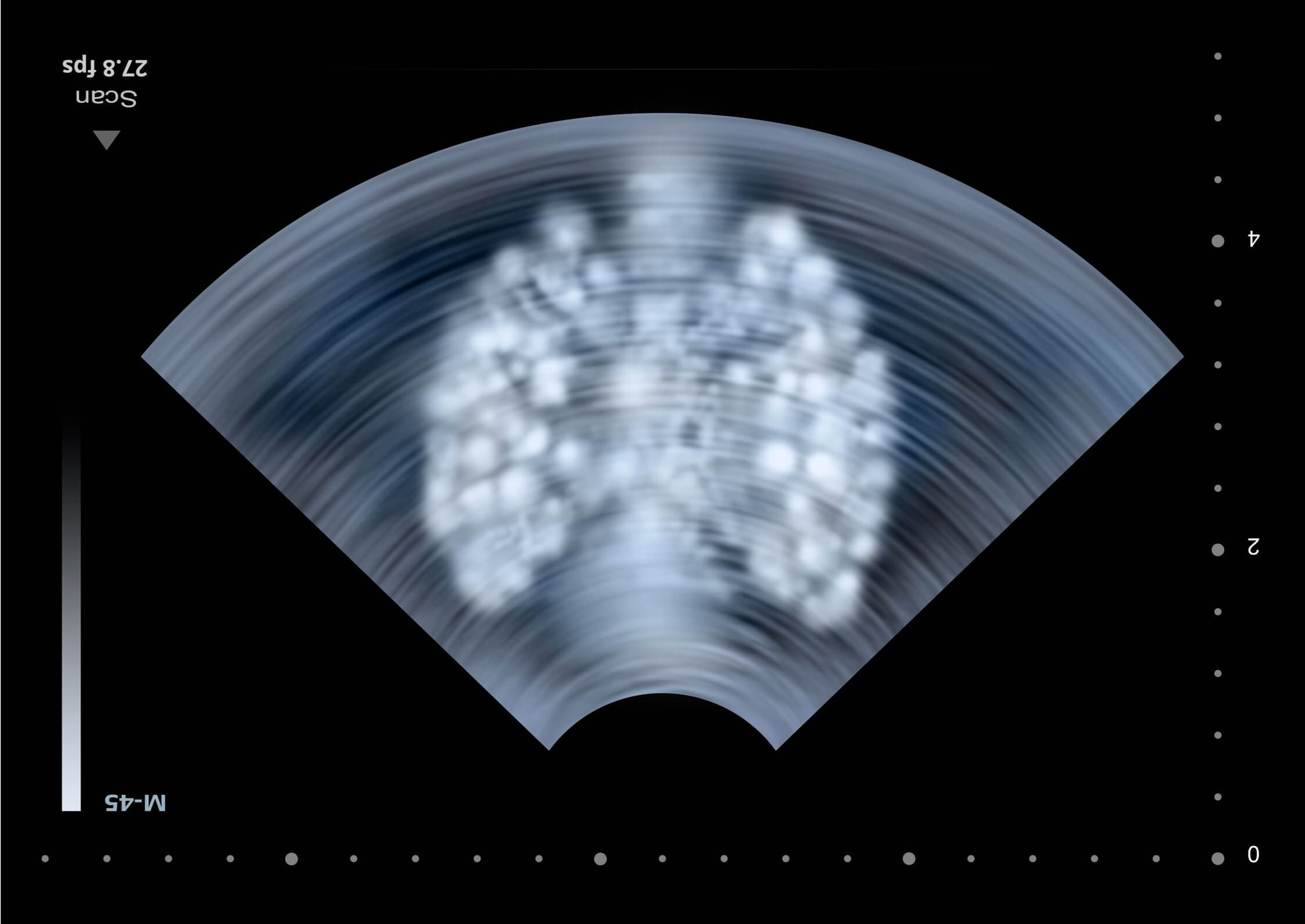
What abnormality is seen here?
Middle aged male, recently hospitalized at outside facility, now presenting with flank pain.
Scroll down for the answer!
Answer: Obstructed ureteral stent with hydronephrosis and hydroureter
The basics:
Stents share sonographic characteristics with most medical tube devices: echogenic double line structure
Ureteral stents should be visible in the bladder and renal pelvis.
Residual hydronephrosis / hydroureter can be compared to prior imaging, if available.
Hydronephrosis / hydroureter makes visualization of stents easier, as they are surrounded by anechoic urine
The more advanced:
Stents may be confused for calcific vessels
Complications of ureteral stents include: migration, malposition, fracture, forgotten stents (not removed when previously scheduled), encrustation, ureteral erosion or fistula formation, or inadequate relief of obstruction
Ureteral encrustation is often associated with indwelling time > 12 weeks (often in forgotten stents), alkaline urine and recurrent urinary tract infections
Patency may be seen with flowing urine at the distal tip of the stent using color doppler
Using color doppler for stent patency has reported sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 83%
Thanks!
-Sonostache Team
Follow us on X, @Sonostache
Follow us on Instagram, @Sonostache
Pepe P, Motta L, Pennisi M, Aragona F. Functional evaluation of the urinary tract by color-Doppler ultrasonography (CDU) in 100 patients with renal colic. Eur J Radiol. 2005 Jan;53(1):131-5.
Geavlete P, Georgescu D, Mulțescu R, Stanescu F, Cozma C, Geavlete B. Ureteral stent complications – experience on 50,000 procedures. J Med Life. 2021 Nov-Dec;14(6):769-775.
Dyer RB, Chen MY, Zagoria RJ, Regan JD, Hood CG, Kavanagh PV. Complications of ureteral stent placement. Radiographics. 2002 Sep-Oct;22(5):1005-22.